Maintaining a healthy gut is crucial for overall well-being and has a profound impact on our physical and mental health. Often referred to as the "second brain," the gut plays a vital role in digestion, absorbing nutrients, and supporting the immune system. It even has the power to influence our mood.
A key communication pathway between the brain and the gut is the vagus nerve. This nerve facilitates the exchange of information, affecting digestion, appetite, and emotions. Moreover, the gut boasts its own network of neurons known as the enteric nervous system, which operates independently of the central nervous system.
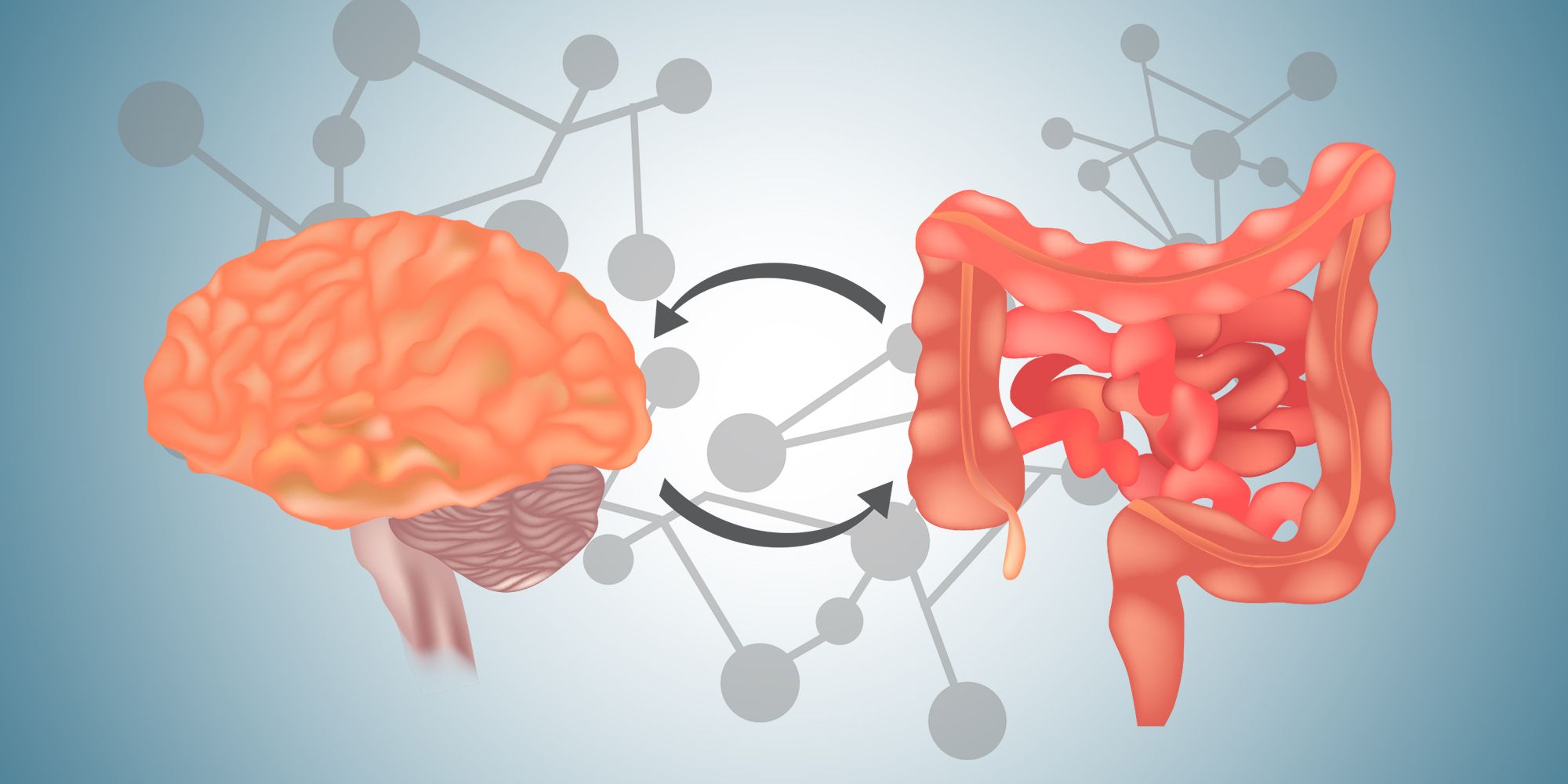
Intriguingly, neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, commonly associated with brain function, are also abundant in the gut. Surprisingly, approximately 95% of serotonin is produced in the intestines. These neurotransmitters play a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions, including mood, sleep, and appetite.
By nurturing our gut health, we can nurture our overall well-being and unlock a harmonious balance within ourselves.
However, when the gut becomes imbalanced, it can lead to various health issues. In this article, we will explore the top ten signs of poor gut health and provide actionable solutions on how to heal your gut.
1. Digestive Issues
One of the most common signs of poor gut health is digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn. These symptoms indicate an imbalance in the gut microbiome, the diverse community of bacteria residing in our digestive tract. An unhealthy gut can lead to difficulty in processing food and eliminating waste, causing discomfort and disruption to daily life.
2. Autoimmune Problems
An imbalanced gut can contribute to autoimmune problems, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body. Conditions such as thyroid issues, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have been linked to poor gut health. The imbalance in gut bacteria can trigger chronic inflammation, weakening the immune system's ability to function properly.
3. Skin Issues
Surprisingly, skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis can be indicative of poor gut health. The gut-skin connection highlights how imbalances in the gut can manifest on the skin's surface. Inflammation caused by an unhealthy gut can disrupt the protective skin barrier, leading to various skin ailments. Addressing gut health can help alleviate these skin issues from their root cause.
4. Sleep Disturbances
Poor gut health can interfere with sleep patterns, leading to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep. The gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin that play a vital role in regulating sleep cycles. An unhealthy gut can disrupt the production of these neurotransmitters, leading to sleep disturbances and fatigue.
5. Mood Disorders
The gut-brain connection is a well-established link between gut health and mental well-being. Studies have shown that imbalances in gut bacteria can impact mood and contribute to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. The gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play significant roles in regulating mood. When bacteria in the gut is imbalanced, it can affect the production of these neurotransmitters, leading to mood disorders.
6. Low Energy Levels
Feeling constantly fatigued or experiencing low energy levels could be a sign of poor gut health. The gut is responsible for absorbing nutrients from the food we consume. When the gut is imbalanced, it may struggle to absorb essential nutrients from certain foods, leading to nutrient deficiencies. These deficiencies can result in decreased energy levels and chronic fatigue.
7. Food Intolerances
Developing sudden food intolerances or sensitivities can indicate the signs of an unhealthy gut. When the gut lining becomes compromised due to imbalances or inflammation, it can become more permeable, allowing undigested food particles and toxins to enter the bloodstream. This can trigger immune reactions and lead to food intolerances or sensitivities.
8. Weight Fluctuations
An imbalance in gut bacteria can contribute to weight fluctuations and difficulties in maintaining a healthy weight. Certain types of gut bacteria are associated with weight loss, increased calorie extraction from food and higher fat storage. Imbalances in these bacteria can lead to weight gain or difficulties in losing weight, even with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
9. Weakened Immune System
The gut plays a significant role in immune system function, as approximately 70% of our immune cells reside in the gut. An unhealthy gut can weaken the immune system's response to pathogens, making individuals more susceptible to infections, allergies, and autoimmune conditions.
10. Brain Fog and Poor Concentration
Brain fog, difficulty concentrating, and impaired cognitive function can be linked to poor gut health. The gut-brain axis allows communication between the gut and the brain through neural, hormonal, and immune pathways. Imbalances in the gut can disrupt this communication, leading to cognitive issues and decreased mental clarity.
Actionable Steps to Improve Gut Health
Eat a Fiber-Rich Diet
Including fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your daily meals is essential for a healthy gut. Dietary fiber acts as fuel for the beneficial bacteria in your gut, promoting their growth and diversity. Aim to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day.

Incorporate Probiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria in fermented foods that confer health benefits when consumed. Yogurt, sauerkraut, kefir, and kimchi are excellent sources of natural probiotics. Including these in your diet can help restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
Consider Digestive Supplements
In some cases, digestive supplements may be beneficial for maintaining gut health. Digestive enzymes, for instance, absorb nutrients and can aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, especially for individuals with digestive disorders or enzyme deficiencies. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any supplements to your routine.
Maintain an Active Lifestyle
Regular exercise not only benefits your physical well-being but also plays a role in improving gut health. Studies have shown that exercise can increase microbial diversity in the gut and reduce inflammation, ultimately promoting a healthier gut environment.

Benefits of a Healthy Gut
1. Enhanced Digestion: A healthy gut and digestive system allows for efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients, ensuring your body receives the essential vitamins and minerals it needs.
2. Boosted Immune System: The healthy gut microbiome, and the immune system are closely linked. A healthy gut microbiota strengthens the immune system, helping to fend off infections and illnesses.
3. Better Mental Health: The gut-brain connection is a fascinating area of research. Maintaining a healthy gut has been linked to improved mood, reduced anxiety, and a lower risk of mental health disorders.
4. Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the body and gastrointestinal tract has been associated with several diseases. By improving gut health, we can reduce inflammation and potentially lower the risk of conditions such as cardiovascular disease and arthritis.
Dietary and Lifestyle Tips for a Healthy Gut
1. Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain additives, preservatives, and unhealthy fats that can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
2. Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut. It helps prevent constipation and supports proper digestion.
3. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut and gastrointestinal health. Incorporate stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.

4. Get Quality Sleep: Sleep plays a vital role in overall health, including gut health. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night to support optimal gut function.
Final Thoughts
Recognizing the signs of poor gut health is the first step towards improving overall well-being. Digestive issues, autoimmune problems, skin issues, sleep disturbances, mood disorders, low energy levels, food intolerances, weight fluctuations, weakened immune system, and brain fog are all indicators that our gut may be imbalanced.
By incorporating actionable solutions such as adopting a diet that supports gut health, managing stress effectively, prioritizing sufficient sleep, regularly engaging in exercise, and considering probiotic supplementation, individuals can take control of their gut health. It's important to remember that a healthy gut is vital for both physical and mental well-being.
Maintaining a healthy gut is a journey that requires patience and consistency. So, stay committed to your efforts and embrace the path towards a healthier gut and a happier you!
References
Harvard Health Publishing - "The gut-brain connection" https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/the-gut-brain-connection
Nature - "Diet–microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism" https://www.nature.com/articles/nature18846
National Library of Medicine - "Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota" https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28165863/








