Are you experiencing mood swings, insulin resistance, or fertility issues? These might be symptoms related to inositol deficiency. Inositol, a natural molecule, plays a crucial role in various biochemical and metabolic functions in our body.
Understanding this deficiency and its potential impact on your health could be the key to unlocking improved well-being. Dive into this comprehensive guide to learn about inositol deficiency symptoms, causes, benefits of supplementation, precautions, and how to choose the right supplement for your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize inositol deficiency symptoms such as mood disorders, insulin resistance and fertility issues.
- Supplementation with myo-inositol may help improve related symptoms by aiding neurotransmitter function, improving insulin sensitivity and addressing hormonal balance.
- Consult a healthcare professional for personalized dosage recommendations to ensure safety when taking an inositol supplement.
Recognizing Inositol Deficiency Symptoms
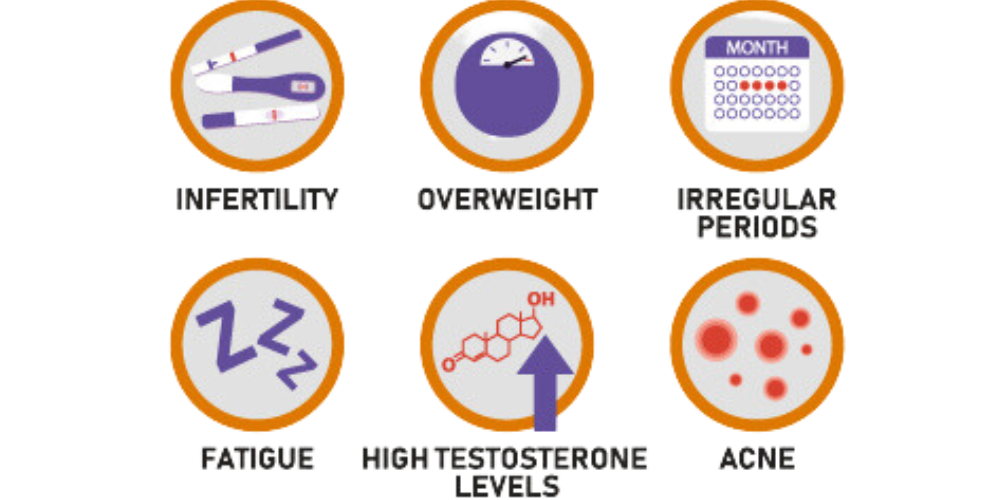
Inositol deficiency can manifest itself in various ways, including mood disorders, insulin resistance, and fertility issues, which may be related to metabolic disorders. It’s important to identify these symptoms for timely treatment and support.
We will delve into each of these symptoms, explaining their potential links to different health conditions.
Mood Disorders
Did you know that mood disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, panic disorder, and anxiety might be connected to low inositol levels in the brain? The biological explanation behind this correlation lies in inositol’s critical role in regulating neurotransmitters and signal transduction pathways in the brain.
Moreover, inositol deficiency has been observed to affect serotonin levels in the brain, which can negatively impact mood and emotional balance.
Several randomized controlled trials have been conducted to study the effects of inositol supplementation on mood disorders, with some studies showing promising results in improving symptoms.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, a key factor in metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can be influenced by inositol deficiency. Essentially, insulin resistance is a state in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin, affecting glucose uptake.
Inositol is involved in the regulation of insulin, reducing glycemia levels, hyperinsulinemia, and improving insulin sensitivity.
Studies have indicated that inositol deficiency could be associated with insulin resistance, and inositol supplementation has demonstrated potential as an intervention for relieving symptoms of insulin resistance. Inositol treatment, therefore, may be worth exploring for those experiencing such issues.
Fertility Issues
Fertility issues, particularly in women with PCOS, may be related to inositol deficiency and its impact on hormonal balance and egg quality. Insulin resistance is a pivotal aspect of PCOS in many patients and is connected with metabolic and reproductive complications. Research has demonstrated that inositol can:
- Improve egg quality in women with PCOS
- Regulate hormone levels
- Induce the synthesis of melatonin
- Enhance oocyte and embryo quality
By addressing inositol deficiency, women with polycystic ovary may experience improved fertility outcomes.
Causes of Inositol Deficiency
Having discussed the symptoms of inositol deficiency, we should now turn our attention to the potential triggers. Inositol deficiency can be caused by factors such as inadequate dietary intake, genetic predispositions, and certain medications.
We will now further investigate each of these causes.
Dietary Factors
A diet low in fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may contribute to inositol deficiency. Myo-inositol, the most common form of inositol, is primarily synthesized in the human kidney. A western diet typically provides around 1 gram of myo-inositol per day.
A balanced diet rich in these food sources is key to maintaining adequate inositol levels and avoiding related issues.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors can also play a role in inositol deficiency. Genetic mutations affecting the synthesis, transport, and absorption of inositol may lead to a deficiency.
For example, mutations in genes associated with myo-inositol synthesis and transport can impede the processes of inositol production and uptake, while mutations in genes coding for inositol transporters can limit the capacity of cells to take up inositol from the surrounding environment.
These genetic mutations can result in imbalances in inositol levels and potentially impact various cellular functions and processes.
Medications
Certain medications, particularly those used to treat bipolar disorder and epilepsy, may deplete inositol levels and affect inositol metabolism. Lithium and valproic acid, both used in the treatment of bipolar disorders, impact enzymes involved in inositol synthesis and recycling, resulting in inositol depletion.
Being mindful of these potential medication-induced deficiencies and consulting a healthcare professional for appropriate management of inositol levels is crucial.
Inositol Supplementation Benefits

Inositol supplementation can counter deficiency and yield multiple benefits including mood enhancement, improved insulin sensitivity, and better fertility. We will now scrutinize each of these benefits to understand the positive impact of inositol supplementation on health.
Mood Improvement
Supplementing with inositol may help alleviate symptoms of mood disorders by supporting neurotransmitter function. Neurotransmitters play a critical role in mood regulation by communicating signals from nerve cells to target cells, thus assisting in the regulation of emotions and impacting mood. Inositol facilitates neurotransmitter function by:
- Regulating neuronal and glial activity
- Participating in signal transduction pathways
- Contributing to the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
Inositol supplementation has shown positive outcomes in improving mood and reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity
Inositol supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity, potentially benefiting those with insulin resistance-related conditions. Studies have revealed that inositol supplements, particularly myo-inositol, can enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance. Research has demonstrated that myo-inositol can reduce insulin resistance by approximately 70% in post-menopausal women with metabolic syndrome.
Inositol’s role in enhancing insulin sensitivity can provide health benefits for individuals dealing with conditions such as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), gestational diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome.
Improved Fertility
Inositol supplements may improve fertility in women with PCOS by:
- Regulating hormonal balance
- Supporting egg quality
- Acting as insulin-sensitizing agents
- Acting as free radical scavengers
- Assisting in the regulation of metabolism
- Promoting ovulation
Particularly, myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol are known to have these effects in PCOS.
By addressing inositol deficiency and its impact on hormonal balance, women with PCOS may experience improved fertility outcomes and a higher likelihood of successful pregnancy.
Precautions and Interactions

When considering inositol supplementation, it is important to be aware of safe dosages, potential side effects, and drug interactions.
Appropriate use of inositol supplements will help you optimize the benefits while limiting any potential risks.
Safe Dosage
The recommended dosage for inositol supplements varies depending on the individual and the condition being treated. It is generally suggested to take 1-4 grams of inositol supplements orally daily, although higher doses have been used in some studies with minimal side effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advised for personalized dosage recommendations.
Adhering to dosage instructions and seeking professional health guidance before consuming high inositol doses is crucial to prevent overdose and associated consequences.
Side Effects
Side effects of inositol supplementation may include diarrhea, gas, and nausea, although it is generally considered safe for most adults. While mild side effects have been reported with higher doses, they tend to be mild and manageable.
As most clinical trials on inositol tend to last no longer than one year, the long-term safety of inositol supplementation is still uncertain. Therefore, it is suggested to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any long-term supplementation.
Drug Interactions
Inositol may interact with certain medications, such as those for diabetes, requiring close monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional. Inositol has the potential to reduce blood sugar levels, so taking it in conjunction with diabetes medications may result in a decrease of blood sugar to a level below the normal range.
Additionally, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist to ascertain if there are any potential adverse reactions or interactions between inositol and specific antidepressants or hormonal birth control methods.
How to Choose an Inositol Supplement

Choosing an inositol supplement involves considering factors such as the form of inositol, the appropriate dosage, and the purity and quality of the product.
Let’s explore these factors in detail and help you make an informed decision when selecting the right supplement for your needs.
Form
Inositol supplements are available in various forms, including myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, which may have different effects on specific health conditions. Myo-inositol has been documented to have a role in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, while D-chiro-inositol is reported to be involved in ovarian function and hormone regulation.
Incorporating myo inositol supplementation into your daily routine may help support these health benefits.
Understanding the distinctions between these forms and their potential therapeutic effects on specific health concerns can guide you in selecting the most suitable inositol supplement for your needs.
Dosage
The appropriate dosage of inositol depends on the individual’s needs and the condition being treated, with consultation from a healthcare professional recommended. For instance, it is generally advised to take approximately 4 grams of inositol per day for insulin resistance, while a dosage of 2000-4000 mg daily is suggested for fertility issues.
Consulting with a healthcare professional can help you determine the most suitable dosage for your specific circumstances.
Purity and Quality
Guaranteeing the purity and quality of an inositol supplement is crucial for safety and effectiveness, hence the importance of choosing a reputable brand and product. When determining the purity and quality of inositol supplements, factors such as the presence of myo-inositol, the absence of contaminants, and the manufacturing process should be taken into account.
Opting for products that are certified by third-party organizations such as NSF International or USP can guarantee that the supplements meet certain standards of purity and quality.
Additionally, verifying if the supplement is produced in a cGMP-certified facility can guarantee quality and compliance with manufacturing standards.
Summary
In conclusion, inositol deficiency can lead to a range of health issues, including mood disorders, insulin resistance, and fertility complications. Understanding the causes behind this deficiency and the potential benefits of supplementation can help you make informed decisions about your health.
Be sure to consult with a healthcare professional and choose a high-quality inositol supplement that suits your individual needs and health conditions. With the right knowledge and approach, you can unlock the potential benefits of inositol supplementation and improve your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What depletes inositol in the body?
Lithium and valproic acid, two widely used antidepressive drugs, can deplete inositol levels in the body. This depletion can lead to psoriasis, and a reduced dietary intake of inositol can also cause deficiency.
What vitamins should you not take with inositol?
No vitamins should be taken with inositol, as no interactions have been found.
What are the symptoms of vitamin b8 inositol deficiency?
Symptoms of a Vitamin B8 (Inositol) deficiency include hair loss, skin problems such as eczema, mental health issues like anxiety and trouble sleeping, constipation, hyperlipidaemia, and muscle weakness.
How do you increase inositol levels?
Increasing inositol levels can be done through the intake of foods such as fruits, beans, grains and nuts, or by taking supplements. The best dosage of inositol for those with PCOS is two grams, twice a day, taken just before meals.
Can inositol supplementation help improve mood disorders?
Yes, inositol supplementation can help improve mood disorders by supporting neurotransmitter function.



